The U.S. expects to see a significant increase in new Electric Vehicle (“EV”) infrastructure projects thanks to a major piece of legislation passed in August of last year.
BHL Bogen

BridgehouseLaw LLP - Your Business Law Firm
Tuesday, December 20, 2022
Expanded EV Incentives for 2023
Monday, November 28, 2022
Mariah Carey - the queen of Christmas?
Since the 1994 release of “All I Want for Christmas is You”, Mariah Carey has become inextricably linked with the Christmas holiday season. Shortly after the release of this song in 1994, it topped the charts in twenty-six countries, including Mexico and Germany. Even now, every year the song surges in popularity as the holidays approach.
Tuesday, November 22, 2022
Beer Ban in Qatar
For many people, beer is one of the first things they associate with a soccer match and an integral part of the stadium experience. Prior to the 2022 FIFA World Cup, the US beer company Budweiser was granted an exclusive license to sell its beer at stadiums in Qatar. However, just two days before the first match of the tournament, Qatari authorities decided to ban beer from all of the World Cup stadiums. Only Bud Zero, Budweiser’s alcohol-free beer, can be sold at the stadiums during the tournament. The only exceptions to this beer ban are designated VIP areas that cost thousands of dollars, and specifically designated FIFA Fan Areas.
Monday, November 07, 2022
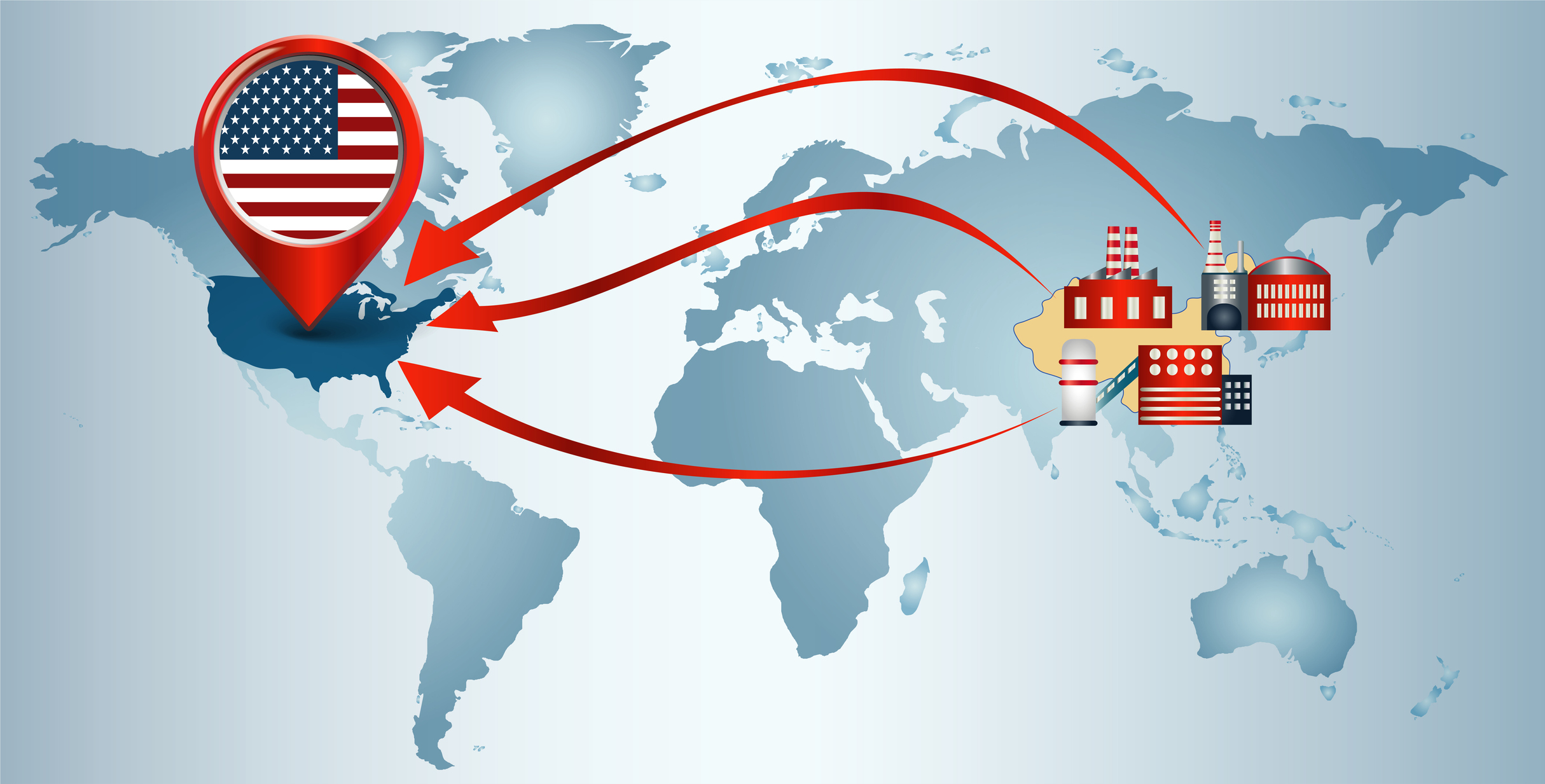
Offshore to Reshore: U.S. Businesses Shift Strategies
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to change the business environment in new ways. We’ve become familiar with some changes, such as increased remote work and disruption to global supply chains. Now, we’re seeing U.S. companies increasingly protect themselves from disruptions by reshoring.
For decades, U.S. companies moved business operations and manufacturing to countries in Asia or Latin America in order to produce under cheaper and more efficient conditions—a process called offshoring. After the COVID-19 pandemic caused the collapse of global supply chains in 2021, manufacturing and distribution in many parts of the world were either interrupted or stopped completely. Numerous U.S. companies were not able to offer their clients their goods anymore because integral components or finished products could not be delivered to the United States. Although supply chain issues have calmed down in recent months, remaining lockdowns continue to affect global supply chains. For example, China, which contributed pre-pandemic roughly 20% of U.S. imports annually, is placing more and more cities under lockdown, which has caused the price of U.S. imports from China to rise dramatically due to supply bottlenecks.
To resolve issues that are ultimately but indirectly caused by the U.S. practice of offshoring, U.S. businesses are increasingly reshoring or bringing manufacturing back to the U.S. in order to decrease dependency on supply chains. The recent trend in reshoring is especially advantageous for small businesses, which do not have the financial resources and endurance to afford doubled or tripled prices for various components they need.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic has catalyzed the shift from offshoring to reshoring, this trend was already emerging before the pandemic hit. Between 2010 and 2020, more than one million jobs were brought back to the United States through reshoring. The COVID-19 pandemic has brought to the forefront the inherent risks of dependence on global supply chains, which can be disrupted by a variety of factors—pandemics, yes, but also political instability and seemingly random events such as the March 2021 blockage of the Suez Canal due to a stuck container vessel.
By turning to reshoring, U.S. companies are demonstrating their ability to adapt, to strengthen supply chain resilience, and to diminish associated vulnerabilities. Reshoring enables businesses to react immediately to the ever-changing needs of the market thanks to the proximity of customers. Shipping costs also decrease through reshoring, although this is partially absorbed by the business to adjust for the higher cost of production in the U.S. due to higher salaries and rent. The rising tensions between China and U.S. is another incentive for U.S. businesses to reshore, as trade policy is ever-changing. For example, recently, the U.S. imposed new restrictions on U.S. companies selling advanced semiconductors to China.
It is important to note that the recent U.S. reshoring trend varies across industries. For example, the textile industry, which requires mostly manual labor, is not likely to return because of the significant wage gap between Asia and the United States.
Although reshoring is considered especially advantageous for small businesses, larger businesses are also reshoring. In December 2021, General Motors announced plans to spend upward of $4 billion USD to expand electric vehicle and battery production in Michigan. Toyota is also about to invest $1.3 billion USD in a battery plant in North Carolina, which is expected to create approximately 1,750 jobs.
Reshoring not only helps to protect U.S. businesses from disruptions, but it also contributes to the U.S. national economy via job creation and development. Federal an
d state governments have therefore been keen to introduce incentives to U.S. businesses partaking in reshoring. Lastly, as U.S. businesses are increasingly scrutinized for their environmental impacts, reshoring manufacturing reduces global fossil fuel consumption from shipping.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic might be about to end, the reshoring trend is expected to remain.
Tuesday, November 01, 2022
Penal Consequences for Putin’s Supporters in Germany?
Could supporters of Russia’s war in Ukraine menace legal consequences in Germany in the future? Since Russia’s attack on February 24, 2022, on Ukraine, many demonstrations have occurred in Germany, mostly in solidarity with the Ukrainian people. But there are also demonstrations organized by members of the huge Russian community in Germany (around 2 million people) and other parties, which support Putin’s side in the war.
Organizing and participating in a public gathering is both in Germany and in the U.S. a constitutional right, even if it occurs in favor of a country that has initiated a war of aggression. But what happens, if pro-Russian demonstrators in Germany start to deny the war crimes that take place in Ukraine?
As a result of German’s WWII reckoning, there is already a criminal law in Germany that prohibits condoning, denying, or trivializing the Holocaust in public or during a public gathering in a way that is likely to disturb the public peace (§ 130(3) Strafgesetzbuch (StGB); German criminal code). Other nations, which penalize the denial of the Holocaust, are Israel and Austria. A similar criminal law does not exist in the United States but such action may constitute grounds for a cause of action under civil law in certain circumstances.
On October 20, 2022, the German parliament voted to amend and extend § 130 StGB. Passage 5 thereof now penalizes condoning, denying, or trivializing genocide, crimes against humanity or war crimes publicly or during a public gathering. To be punishable under the amended § 130(5) StGB, an act must relate to a certain national, racial, religious, or ethnic group in a way that is likely to incite someone to hate or act with violence against this group or members of this group or to disturb the public peace. The passed bill provides for fines as well as imprisonment up to three years, whereas the maximum imprisonment for sanction regarding the Holocaust in § 130(3) StGB is five years. The rationale behind this discrepancy is the significance of the Holocaust in German history, which justifies more severe penalties.
According to statements by politicians with expertise in law, it is now possible that pro-Russian supporters could be penalized based on this new law if they, for example, condone or deny war crimes committed by Russian soldiers during a demonstration.
Notably, the new law does not prohibit a person from denying that a specific war constitutes a crime of aggression. The crime of aggression, which is aggression that constitutes a manifest violation of the Charter of the United Nations as determined by its character, gravity, and scale, is penalized as a crime under international law (§ 13 Völkerstafgesetzbch (VStGB); Code of Crimes against International Law). As such, whether a war constitutes a crime of aggression under § 13 VStGB is, to some extent, a subjective assessment. Because the new § 130(5) StGB does not prohibit a person from denying that war is a crime of aggression, such assessments should not be stymied and will not be punished.
Despite possible consequences to pro-Russian demonstrators, the war in Ukraine did not cause the amendment to § 130 StGB. Rather, the amendment to § 130 StGB results from the European Commission’s initiation of initiated treaty violation proceedings against Germany in December 2021. In the European Commission’s opinion, Germany violated the EU resolution 2008/913/J1 from November 28, 2008, which aimed to fight specific forms and expressions of racism and xenophobia.
Although the newly-amended law might affect upcoming demonstrations, the actual coverage of § 130(5) StGB will be determined by the court's decisions.
Tuesday, October 25, 2022
Breast Cancer Awareness Month
As fall begins and the leaves change, people and businesses turn their attention to the vital issue of breast cancer. According to the World Health Organization, breast cancer is the world’s most common cancer, accounting for 12% of new cancer cases worldwide in 2021. While breast cancer is caused by genetic abnormalities, only 5-10% of breast cancers are caused by abnormalities inherited from parents. The remaining 85-90% of breast cancers are due to genetic abnormalities resulting from the aging process. For this reason, 1 in 8 U.S. women will develop invasive breast cancer during their lifetime. Given the disease's broad impact, breast cancer charities have been working for decades to increase awareness and raise the funds necessary to fight back.
Each October people around the world participate in Breast Cancer Awareness Month, an international health campaign created to raise awareness and funds for research, prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and cure of breast cancer. Throughout the month, major breast cancer charities across the globe host a variety of events to raise awareness and show support to all those who have been affected by breast cancer. From providing free informational material to hosting discussions by survivors, October is full of activities and resources that support any level of involvement.
For those looking to participate in Breast Cancer Awareness Month, the National Breast Cancer Foundation has a host of information and resources on its website. In addition, to fundraising and outreach, you can check with your local breast cancer charity about events in honor of National Metastatic Breast Cancer Awareness Day on October 13, and National Mammography Day on October 21. Finally, you can show support for all those who have fought and continue to fight against breast cancer by wearing pink and displaying the pink ribbon around your office all month long. No matter how you participate, each contribution makes a difference so talk to your local breast cancer charity about getting involved today.
Wednesday, October 12, 2022
Bunnycide in Switzerland?
monetary compensation to Lindt.
Thursday, September 08, 2022
The German Act on Corporate Due Diligence Obligations in Supply Chains
1. “Heal the world”?
On January 1, 2023, the German “Lieferkettensorgfaltspflichtengesetz (LksG)”, Act on Corporate Due Diligence Obligations in Supply Chains will come into force. This will mark a milestone within the EU to fight slave-like working conditions and vice versa to protect human rights worldwide. According to the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development, globally 79 million children suffer from exploitative working conditions and 25 million children provide forced labor. Since the appeal by the German government to incorporate due diligence instruments voluntarily was largely unsuccessful, the legislature now makes its former suggestions mandatory.
The goal of the LksG is to require the companies that trade and sell goods produced in other nations to run background checks on their suppliers to prevent European wealth based on exploitation.
2. Structure
a. Companies that must adhere to the LksG
The LksG will initially apply only to companies that employ at least 3,000 people globally regularly. Companies that have either their principal place of business, their branch office, their administration, or their registered office in Germany must abide by the LksG. Companies that have at least a branch office under Section 13d German Commercial Law Code in Germany must comply as long as their 3,000 employees are employed in Germany.
b. Definitions
According to Section 3 of the LksG, companies must adhere to due diligence obligations in an “appropriate manner” to minimize risks regarding human rights and environmental violations. Section 2 lists and clarifies the risks that the LksG aims to mitigate, referencing various international agreements. Central aspects of human rights protections in the LksG include:
(1) Prohibition of forced and slave labor and slavery;
(2) Employee rights, including occupational and safety as well as organizational and trade union rights;
(3) Prohibition of discrimination and unequal treatment; and
(4) Compliance with environmental standards and other environmental rights.
Environment-related aspects of the LksG aim to conserve the location of production as a habitat for the local population by reducing pollution. As such, the LksG uses the nexus of environmental rights to further its central goal: human rights protection.
There is a presumption that the risk for human rights, as defined in the LksG, is present if certain threshold facts exist that increase the likelihood of a violation. For instance, if there is evidence of employment of children, compulsory labor, or worker’s protection rules at the workplace.
c. Duties and Consequences
(1) Risk Analysis and Management
The first step for each company will be to implement compliance measures to evaluate the likelihood of the event, that risk as defined in Section 2 of the LksG exists within the supply chain. After this evaluation, a detailed plan outlining concrete measures to minimize risks must be created. The third step includes the implementation and thus, preventive measures for the future as well as actions to rectify already existing infringements.
(2) Compliance Mechanisms
First, companies themselves must assess the effectiveness of their risk prevention on an annual basis. Consequently, they have to publish on their website a report on their efforts to minimize human rights violations within their supply chain. Public opinion is considered equally important to company management as economic risks through fines. Second, companies are required to establish a complaint process to report violations of human rights or lack of compliance with environmental protection rules. Third, section 11 grants third parties, such as NGOs, the ability to file complaints for those who suffer due to the company’s insufficient practices. This should put an early end to corporate secrecy due to the investigatory practices of NGOs.
Fourth, there are specialized authorities to investigate and evaluate regularly whether all the measures required by the LksG have been implemented.
(3) Liability of Companies and Suppliers
Of course, companies will not be liable for any violation of human rights on this planet. Companies will only be responsible for what they can control within their supply chain. The supply chain consists of all products and services a company offers and includes any step necessary to produce or provide a service. Therefore any act of a direct or indirect supplier is ascribed to the obligated companies. Misconduct by either the company or by a supplier can have severe consequences: Primarily, companies that lack their own motivation to comply must pay fines of up to two percent of the company’s annual worldwide revenue. Further, an infringement can lead to the company becoming
ineligible for public contracts in the future. The degree of liability depends on the chance of knowing about the infringement and the opportunity to rectify the infringement. In this evaluation, the differentiation between direct and indirect suppliers is relevant. There is little to no chance of escaping liability if the respective supplier is active in a region or profession where human rights or environmental risks are common.
It is impossible to prevent any violation from happening and minimize any risk to zero due to the reliance on third-party actors. The liability, therefore, is excluded if the obligor company has acted by the LksG.
3. What to Expect
In February 2022, the European Commission accepted an official recommendation by the European Parliament to issue a guideline with even further requirements. Thus, a unified EU regulation is likely to come sooner rather than later. As soon as January 1, 2024, the current act in force will apply to companies with not 3,000, but 1,000 employees.
Monday, May 09, 2022
The USCIS Has Automatically Extended Noncitizen Work Permits For 540 Days For Certain Renewal Applicants
The USCIS Has Automatically Extended Noncitizen Work Permits For 540 Days For Certain Renewal Applicants
The U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) has announced a Temporary Final Rule (TFR) that will temporarily amend an existing regulation set forth by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). This TFR will increase the automatic extension time for Employment Authorization Document (EAD) renewals from 180 days to 540 days from the expiration date stated on their EADs. The increased extension began on May 4th and is designed to avoid employment gaps for non-US citizens who need to renew their EADs and stop the interruptions of employers who rely on noncitizen workers.
The automatic extension will end either at the end of the 540-day period or upon the notification of a final decision on the EAD renewal application, whichever comes first. The extension is granted only to those who were already eligible for the 180-day extension while their renewal applications are pending.
For individuals who filed for an EAD renewal and their 180 days have already ended, they are granted a new extension of 540 days and may resume employment. The new extension for EADs is set to expire on October 27th, 2023.
For more updates on employment, immigration, international business, and more, follow along with our blog.
Wednesday, April 20, 2022
Ferrero Recall
Ferrero Recall
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that Ferrero U.S.A., Inc. will recall two of its chocolate products sold in the United States. The recalls were voluntary and were due to potential salmonella contamination. Although this recall may be disappointing or concerning to some chocolate lovers, this voluntary recall was a smart business move by Ferrero that potentially saved them from later liability.
This recall comes out of an abundance of caution after roughly 100 salmonella cases were reported from their products in Europe. Both the chocolates in the US and Europe are manufactured in the same facility in Belgium.
The two chocolate products being recalled in the US are the Kinder Happy Moments Chocolate Assortments and the Kinder Mix Chocolate Treats Basket. The recall includes all of these products in the US with a best before date up to October 7th, 2022.
Though it may have been disappointing to have to recall thousands of products before one of the largest chocolate buying days of the year, Ferrero make a wise decision. When importing goods overseas, businesses must make sure that their quality control is impeccable.
Ferrero had a lapse in their quality control and must fix it, but the recall, if instituted properly, could protect them from some kinds of liability if someone becomes sick from eating their product. If the recall is conducted poorly, the recall could increase the chances of liability.
It is vital to have a recall plan in place for your products before it is ever needed, that way you can act fast, have a consistent message, and correct the issue.
If you are in need of recall planning legal consultants, contact our team at BridgehouseLaw.
To get more updates on international stories related to business, law, immigration, and more, check out our blog.
Monday, April 11, 2022
Changes to the EB-5 Investor Visa Program
Changes to the EB-5 Investor Visa Program
The EB-5 Reform and Integrity Act of 2022 was recently signed into law making major changes to the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program. These changes include raising the minimum investment amount and reauthorizing the EB-5 Regional Center Program
What is an EB-5 Visa?
The EB-5 program is a visa program administered by the USCIS to allow foreign investors, their spouses, and unmarried children under 21 to become eligible to apply for permanent residence in the United States if they:
Invest substantial capital in order to finance a business in the United States that will provide substantial economic growth by creating at least 10 jobs.
Or
Invest in government authorized “Regional Centers”.
The second option is quite popular among investors due to the ability put money towards a regional center with a pool of other investors without having to worry about the risk of the business failing or employment problems.
Minimum Investment Requirements
The new act raises the minimum investment requirements to $1,050,000 or $800,000 if the investor chooses to invest in targeted employment areas (TEAs).
Targeted employment areas are found in rural areas with high unemployment rates.
Regional Center Program
The EB-5 Regional Center Program lapsed in June of 2021 but was revived in March of 2022 for at least 5 years, until 2027. The goal of the EB-5 program is to simultaneously increase foreign direct investments and boost the economy by creating more jobs in the United States.
Though being a much more passive investment, the EB-5 Regional Center Program is still an investment that ultimately still leads to economic growth and job creation. A list of USCIS approved EB-5 Immigrant Investor Regional Centers can be found here.
Contact our Charlotte immigration team for more information about the EB-5 visa.
For more updates on immigration, visas, international business, and more, read out blogs here.
Monday, March 21, 2022
Changes to the EB-5 Investor Visa Program
Changes to the EB-5 Investor Visa Program
The EB-5 Reform and Integrity Act of 2022 was recently signed into law making major changes to the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program. These changes include raising the minimum investment amount and reauthorizing the EB-5 Regional Center Program
What is an EB-5 Visa?
The EB-5 program is a visa program administered by the USCIS to allow foreign investors, their spouses, and unmarried children under 21 to become eligible to apply for permanent residence in the United States if they:
Invest substantial capital in order to finance a business in the United States that will provide substantial economic growth by creating at least 10 jobs.
Or
Invest in government authorized “Regional Centers”.
The second option is quite popular among investors due to the ability put money towards a regional center with a pool of other investors without having to worry about the risk of the business failing or employment problems.
Minimum Investment Requirements
The new act raises the minimum investment requirements to $1,050,000 or $800,000 if the investor chooses to invest in targeted employment areas (TEAs).
Targeted employment areas are found in rural areas with high unemployment rates.
Regional Center Program
The EB-5 Regional Center Program lapsed in June of 2021 but was revived in March of 2022 for at least 5 years, until 2027. The goal of the EB-5 program is to simultaneously increase foreign direct investments and boost the economy by creating more jobs in the United States.
Though being a much more passive investment, the EB-5 Regional Center Program is still an investment that ultimately still leads to economic growth and job creation. A list of USCIS approved EB-5 Immigrant Investor Regional Centers can be found here.
Contact our Charlotte immigration team for more information about the EB-5 visa.
For more updates on immigration, visas, international business, and more, read out blogs here.
Temporary Protected Status For Ukrainians in the US
Temporary Protected Status For Ukrainians in the US
Last week, the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) announced the designation of Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for Ukraine, specifically Ukrainian nationals living in the United States. The Temporary Protected Status lasts for 18 months at which time, the DHS will have the choice to either extend the TPS or redesignate Ukraine.
The decision to designate Ukraine as a Temporary Protected Status comes after the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The goal of the TPS is to protect Ukrainian nationals in the US from having to leave and go back to Ukraine.
To qualify for the Temporary Protected Status, Ukrainian nationals must have continuously resided in the US as of March 1st, 2022. Ukrainian nationals who arrived in the US after March 1st or were not living in the US continuously, are not eligible for TPS.
Ukrainian nationals who receive TPS must also apply to the US Citizenship and Immigration Services within 180 days. They are also able to apply for Employment Authorization Documents (EADs) which would allow them to work in the United States lawfully.
“Russia’s premeditated and unprovoked attack on Ukraine has resulted in an ongoing war, senseless violence, and Ukrainians forced to seek refuge in other countries,” said Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas, the Secretary of the Department of Homeland Security.
For a country to be designated for Temporary Protected Status, the country’s conditions must fall into at least one of the three following situations: ongoing armed conflict, environmental disasters, or extraordinary and temporary conditions.
To learn more about topics related to international business, law, immigration, current events, and more, check out our other blogs.
Thursday, March 10, 2022
New Automatic Extension of Employment Authorization for E-visa Dependent Spouses

New Automatic Extension of Employment Authorization for E-visa Dependent Spouses
USCIS policy alert from November 12, 2021, states that the employment authorization procedure for E and L nonimmigrant dependent spouses will become automatic.
What does this change mean?
USCIS will consider E and L dependent spouses to be employment authorized for the duration of their valid E or L status, which is determined by the visa holder’s I-94.
Significance of the I-94 “Admit Until Date”
The “Admit until Date” on the I-94 determines the duration of the valid E or L status, not the expiration date listed on the E or L visa. The “admit until date” is the date the visa expires. Visa holders are not authorized to work beyond the “admit until date” on their I-94 without extension or application to change status.
Significance of the E-Visa Expiration Date
The expiration date listed on the E or L visa is the last day that the visa holder may travel to a port-of-entry in the United States.
When will the change, which grants E and L visa dependent spouses employment authorization incident to status, take place?
This change will take place once the Department of Homeland Security revises the Forms I-94 evidencing nonimmigrant status so that E and L dependent spouses are distinguished from E and L dependent children on the face of the document. The revised Form I-94 will contain a notation indicating that the bearer is an E or L dependent spouse.
Interim Measures
The guidance released by USCIS on November 12, 2021 is effective immediately.
Until the USCIS revises the I-94 to delineate between dependent spouses and dependent children, is there an automatic extension for E and L dependent spouses?
Yes. Until the USCIS revises the I-94 to delineate between dependent spouses and dependent children, the automatic extension of employment authorizations for E and L dependent spouses will at the earlier of three dates:
- the “Admit Until Date” on the visa holder’s I-94, since this indicates the end of the visa holder’s valid nonimmigrant status;
- the approval or denial of the EAD renewal application; or
- 180 days from the expiration of the previous EAD.
What papers can I present to prove employment authorization until the USCIS revises the I-94 for Form I-9 purposes?
The following combination of documents is sufficient to prove employment authorization:
(1) an unexpired Form I-94;
(2) a Form I-797C (Notice of Action) showing a timely-filed EAD renewal application in the (a)(17) or (a)(18) categories; and
(3) a facially expired EAD under the same category.
If you have further questions, please email caitlin.becker@bridgehouse.law
or call (980) 219-5200.
Land and Ferry Travelers to the US No Longer Need to Present a Negative COVID-19 Test to Enter
Land and Ferry Travelers to the US No Longer Need to Present a Negative COVID-19 Test to Enter
The US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has announced a minor change to travel restrictions regarding land travel and ferry ports of entry.
In December, the DHS announced that they would restrict land and ferry travel to only vaccinated travelers, individuals under the age of 18 or lawful US residence could enter the United States by land or ferry. This announcement made it so that unvaccinated essential travelers were no longer allowed to enter the United States. You can read more on that in our previous blog.
All vaccinated travelers, individuals under the age of 18, and lawful US residents were also required to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test.
New Announcement
Now, the Department of Homeland Security has announced that individuals entering the United States via land or ferry are no longer required to show proof of a negative COVID-19 test. They only need to present proof of vaccination.
This announcement will surely make it easier for travelers to enter the US through land or ferry by allowing them to save time not having to take a test before entering. This new announcement only applies to land and ferry travel for not, but it may set a precedent for how air travelers will be able to enter the United States in the near future.
Check out more of our blogs for news on international business, law, travel, and more.
H-1B Visa Denials Dropped In 2021
H-1B Visa Denials Dropped In 2021

H-1B Visa application denial rates have dropped significantly in 2021 with only 4% of applications being denied. This was down from a denial rate of 13% in the year before.
The H-1B visa is an employment-based, temporary work, non-immigrant visa. This visa offers companies the opportunity to bring highly skilled, credentialed foreign citizens into the U.S. for employment in a specialty occupation for up to 6 years. After the H-1B expires, the visa holder can reapply.
The company, as the employer, must sponsor the H-1B applicant. These visas are only available for a short period, so the sponsors and applicants must be ready to apply within the allocated window. The list of H-1B occupations is broad, but some level of knowledge and at least a bachelor’s degree or its equivalent is required. Some examples of these specialty occupations include:
- Engineers
- Accountants
- IT Professionals
- Architects
- Educators
And many more.
H-1B Visa Application
The sponsoring employer must submit a Labor Conditions Approval (LCA) to the Department of Labor and register for the H-1B lottery if the application is subject to the H-1B cap. Once the LCA is approved and if the application is selected in the lottery (if necessary), the employer will submit a Form I-129 to USCIS, along with required fees, documentation, and the applicant’s resume and work qualifications.
On March 1st, 2022, the USCIS will begin to accept H-1B Visa applications for the 2023 fiscal year. The 2023 fiscal year begins on October 1st, 2022.
Fees
A general list of H-1B fees include:
- Registration fee – $10
- Base filing fee – $460
- ACWIA fee (for employers with 25 or fewer full-time employees) – $750 OR ACWIA fee (for employers with 26 or more full-time employees) – $1,500
- Fraud Prevention and Detection fee – $500
- Public Law 114-113 fee (only for companies with over 50 employees where more than half of the employees are under H-1B/L1 status) – $4,000
- Premium Processing fee (optional) – $2,500
Obtaining an H-1B visa is often confusing and difficult for the applicant, as well as the employer sponsor. At BridgehouseLaw, we make that process easier by guiding the sponsor every step of the way through the application process. If you would like help in filing for an H-1B, contact us! We would be happy to help.
The Department of Homeland Security Has Announced Tighter Travel Restrictions for 2022
The Department of Homeland Security Has Announced Tighter Travel Restrictions for 2022

The US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has announced that they will tighten COVID-19 travel restrictions on travelers from Mexico and Canada at land ports of entry (POEs) and ferry terminals.
As you can read about in our last article about the November 8th travel policy, the only ways for individuals to enter the United States by land or ferry were to be:
- Under the age of 18 (under the required age to be vaccinated)
- A US citizen or hold a permanent US resident
- A fully vaccinated traveler as described here
- Or an essential traveler, which included persons on diplomatic or official foreign government travel, persons traveling to the US for public health/infrastructure purposes, and more.
In January, the DHS plans on removing unvaccinated essential travelers from the list making it so that only individuals under the age of 18, US citizens/permanent residents, and vaccinated travelers can enter the United States via land and ferry.
Even for essential purposes, unvaccinated travelers over the age of 18 and who aren’t permanent residents will not be able to cross the border into the United States.
There is no official start date for this policy as of yet. We will update you once the start date is announced.
Manufacturing SMEs are Among the Hardest Hit by the Supply Chain Problems
Manufacturing SMEs are Among the Hardest Hit by the Supply Chain Problems

All across the world over the last several months, supply chain problems have hit many industries hard. Some of the most famous examples of this include Chick-Fil-A being short on sauces and Wingstop running low on chicken wings. But those are just a couple of examples. What’s not making news are the thousands of SMEs that are not receiving their supplies.
SMEs stand for small and mid-sized enterprises. There are over 30 million SMEs in the US, making up over 99% of all US businesses. SMEs also employ almost 50% of America’s total workforce.
Small to mid-sized enterprises are the ones who are hit the hardest by the supply chain issues, and most of all, manufacturing businesses. Studies have shown that nearly 50% of manufacturing SMEs will have to find new supply chain options within the next six months and many are having difficulties finding alternative suppliers.
Why is this happening to SMEs?
The supply chain is affecting most industries and businesses that rely on receiving supplies from outside sources. Even the big businesses are being affected by this, but, unlike small businesses, large corporations have more means to get around these issues, including using air freight and seemingly unlimited capital to make up for it.
SMEs, especially small manufacturing businesses do not have this option and are getting pushed farther and farther back on the priority list.
This isn’t just happening in the US either. All across the EU and UK, small to mid-sized businesses are struggling to get their supplies.
The supply shortages combined with labor shortages, inflation, and the pandemic have all taken a toll on these businesses.
The US Federal Government is trying to identify and solve supply chain issues. The Federal Trade Commission has ordered major wholesale and retail corporations to share their supply chain data. A few of those corporations include Amazon, Proctor & Gamble, and Walmart. The FTC’s goal is to dissect the data to find the problems and hopefully the solution to the supply chain crisis.
Read more of our blogs for up-to-date information about international business, law, and much more!